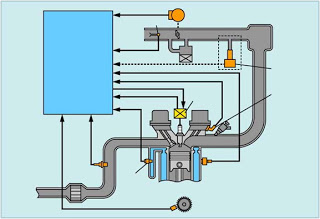
Technology Automotive – 12 Types Indicators Car Type Instrument Panel Function – Indicator lights are widely used on cars and motorcycles for the driver’s pointer or reminder when operating the car, then through that Indicator we can control the instrument panel of the car dashboard so that the driver gets a clue about the condition of the car at that time. Indicator lights are not something new in car engines and motor engines because every car and motor manufacturer has made the device in such a way as to be easy to understand, but not all drivers understand the instructions indicated to them. Some even consider the lights are just decorations that embellish the instrument panel.
Therefore recognize and understand the information we convey may be useful ie 12 functions of the work system Indicator lights one of which is the indicator lights Belt Seat Belt that flashes or even sounds for more details about the details of each function of the indicator light below is the meaning of some common Indicators encountered on the instrument panel:
1. Safety Belt Indicator:
This indicator is a warning to use the seat belt. Generally This indicator will continue to glow, blink or sound as long as the Safety Belt is not used. When you are ready to drive, you should immediately use the Safety Belt for your safety and also avoid a ticket.
2. Remote Light Indicator:
This indicator indicates that the High Beam (High Beam) is in use. If not needed immediately turn off because these lights dazzle and disrupt the eyesight of other riders and can cause accidents.
3. Car Door Indicators:
This indicator indicates that the car door is still open (not completely closed). In some vehicles can be more specific, such as the front door, rear, left or right.
4. Fuel Indicators:
If this indicator is on, indicates that the gasoline supply in your car tank is running low. Immediately perform charging at the nearest gas station.
5. Indicator Air bag:
This indicator indicates that there is a problem with the Airbag system. Because the Airbag is connected with many sensors and computers, then make repairs in the official workshop.
6. Parking Brake Indicators:
When you use Parking Brake (Parking Brake), this indicator will light up. Reminds you to take it off before running the car.
7. Brake Indicators:
This indicator indicates that there is a problem with Rem. Because the braking system is one of the vital parts, then immediately check the problem to prevent the occurrence of disaster.
8. Indicator ABS:
If your car has an ABS braking system and the Indicator Light is on, then it indicates a problem with the ABS system. Although the ABS system is problematic, the brakes continue to work (in the conventional way), but allowing them to dissolve can make repair costs swell.
9. Accu Indicator:
When this Indicator is on, it does not mean there is a problem with the car battery, but on the car’s electrical system, such as the alternator performance problems, the regulator, and the connecting cables are not optimal.
10. Engine Temperature Indicators:
This indicator indicates the engine temperature or radiator is too high. There are also two colors, namely green (normal temperature state) and red (the state of high temperature / over heat). If this Indicator lights up when driving immediately pull over and turn off the engine.
11. Oil Pressure Indicators:
If this indicator is on, indicates that the oil pressure is low (oil volume decreases). This is a serious problem and can cause damage to the car engine. This problem can be caused by several things such as failure of oil pump function and so on.
12. Check Engine Indicator:
This indicator indicates that there is a component of the machine that is not working properly. These components may be sensors or other components that support the overall workings of the machine.
__________________________________________________________
12 Types Indicators Car Type Instrument Panel Function
The instrument panel of a car, often referred to as the dashboard, contains various indicators and warning lights that provide vital information about the vehicle’s status and operation. Here are 12 common types of indicators and their functions:
- Check Engine Light (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
- Function: Indicates an issue with the engine or emissions system.
- Action: Requires diagnostic attention to identify and fix the problem.
- Battery Warning Light
- Function: Signals a problem with the charging system, such as a failing battery or alternator.
- Action: Check the battery and charging system immediately.
- Oil Pressure Warning Light
- Function: Warns of low engine oil pressure, which could cause serious engine damage.
- Action: Stop the vehicle and check the oil level; add oil if necessary.
- Brake System Warning Light
- Function: Indicates issues like low brake fluid, a problem with the braking system, or that the parking brake is engaged.
- Action: Address immediately, especially if the light persists after releasing the parking brake.
- ABS Warning Light (Anti-lock Braking System)
- Function: Signals a malfunction in the ABS.
- Action: The brakes will still work, but the ABS may not function properly; have it checked.
- Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) Light
- Function: Alerts to low tire pressure in one or more tires.
- Action: Check and inflate tires to the recommended pressure.
- Coolant Temperature Warning Light
- Function: Warns of an overheating engine.
- Action: Stop the vehicle and let the engine cool; check coolant levels.
- Seat Belt Reminder Light
- Function: Alerts that the driver or passengers have not fastened their seat belts.
- Action: Buckle all seat belts.
- Airbag Warning Light
- Function: Indicates a fault in the airbag system.
- Action: Have the system inspected to ensure airbags will deploy in an accident.
- Fuel Level Indicator
- Function: Alerts when the fuel level is low.
- Action: Refuel soon to avoid running out.
- Door Ajar Warning Light
- Function: Indicates that one or more doors are not fully closed.
- Action: Check and close all doors securely.
- Traction Control System (TCS) or Stability Control Light
- Function: Signals the system is active to maintain traction or indicates a fault.
- Action: If it flashes during slippery conditions, it’s normal. If it stays on, check for system issues.
These indicators vary by car model, and it’s essential to refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific details on each light and its meaning.
Check Engine Light (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
Check Engine Light (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
Appearance:
- Typically an icon resembling an engine, often yellow or orange in color.
- May include text such as “CHECK ENGINE” or “SERVICE ENGINE SOON.”
Function:
- The check engine light (CEL) illuminates when the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics (OBD) system detects a problem with the engine or emissions control systems.
- It can indicate a minor issue (e.g., a loose gas cap) or a serious problem (e.g., engine misfire, catalytic converter failure).
Common Causes:
- Loose or Faulty Gas Cap:
- A loose or damaged gas cap can cause fuel vapors to leak, triggering the light.
- Oxygen Sensor Failure:
- The sensor monitors the amount of unburned oxygen in the exhaust.
- Mass Airflow Sensor Issues:
- This sensor measures the air entering the engine for proper fuel mixture.
- Spark Plug or Ignition Coil Problems:
- Faulty spark plugs or ignition coils can cause misfires.
- Catalytic Converter Problems:
- Failure can result in increased emissions and reduced engine performance.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve Issues:
- The valve helps reduce emissions by recirculating exhaust gases.
- Vacuum Leak:
- A leak in the engine’s vacuum system can disrupt air-fuel balance.
- Faulty Sensors or Wiring:
- Problems in various engine-related sensors or electrical connections.
What to Do When It Lights Up:
- Check for Simple Issues:
- Tighten the gas cap if it’s loose. Drive for a while to see if the light turns off.
- Monitor Vehicle Performance:
- If the vehicle runs normally, it may not be an urgent issue, but it still needs attention.
- If you notice poor acceleration, stalling, or other performance issues, avoid driving and seek help immediately.
- Use a Diagnostic Scanner:
- A code reader can pull error codes from the OBD system to identify the problem.
- Visit a Mechanic:
- If you’re unsure or if the issue persists, take the car to a qualified technician.
Flashing Check Engine Light:
- Indicates a severe issue, such as an engine misfire, which can cause significant damage.
- Stop driving immediately and get the vehicle serviced.
Preventive Measures:
- Perform regular maintenance, including oil changes, filter replacements, and spark plug checks.
- Address minor issues promptly to avoid bigger, costlier problems.
Car Battery Warning Light
Car Battery Warning Light
Appearance:
- A red icon resembling a car battery with positive (+) and negative (-) symbols.
Function:
The battery warning light indicates an issue with the vehicle’s charging system, not just the battery. When illuminated, it typically means the alternator isn’t charging the battery properly or there’s another problem in the electrical system.
Common Causes:
- Faulty Alternator:
- The alternator generates electricity to charge the battery and power electrical systems. A failure can trigger the warning light.
- Damaged Battery:
- An old or failing battery may not hold a charge, causing the system to detect an issue.
- Loose or Corroded Battery Connections:
- Poor contact can interrupt the flow of electricity.
- Drive Belt Issues:
- A broken or slipping drive belt can prevent the alternator from working properly.
- Faulty Voltage Regulator:
- The regulator ensures the alternator charges the battery at the correct voltage. Malfunctions can cause overcharging or undercharging.
- Wiring Problems:
- Loose, frayed, or damaged wiring in the charging system can disrupt its functionality.
What to Do When the Battery Light Turns On:
- Check for Immediate Symptoms:
- Dim headlights, flickering dashboard lights, or difficulty starting the engine are signs of a failing charging system.
- Turn Off Non-Essential Electrical Devices:
- Reduce the load on the battery by turning off accessories like the radio, air conditioning, and heated seats.
- Inspect the Battery Connections:
- If you’re comfortable, check if the battery terminals are tight and free of corrosion.
- Drive to Safety:
- The vehicle can run briefly on battery power, but it won’t last long. Head to a safe location or repair shop as soon as possible.
- Avoid Restarting the Engine:
- If the battery is nearly depleted, restarting the engine may not be possible.
When to Seek Immediate Help:
- The vehicle stalls or struggles to stay running.
- Electrical components, such as lights or the radio, fail completely.
- The warning light stays on after restarting the car.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Maintenance:
- Inspect the battery and alternator during routine servicing.
- Replace Old Batteries:
- Batteries typically last 3-5 years. Replace them before they fail.
- Check Belts and Connections:
- Ensure the drive belt is in good condition and connections are clean and secure.
- Monitor for Early Signs:
- Address flickering lights or difficulty starting the engine promptly.
A proactive approach can help avoid being stranded with a dead battery or failing charging system!
Car Oil Pressure Warning Light
Car Oil Pressure Warning Light
Appearance:
- An icon resembling an oil can with a drop of oil falling from its spout, typically red.
Function:
The oil pressure warning light indicates low oil pressure in the engine. Proper oil pressure is essential to lubricate engine components and prevent overheating or damage.
Common Causes:
- Low Oil Level:
- Insufficient oil in the system due to leaks, burning oil, or extended intervals between oil changes.
- Oil Pump Failure:
- The pump is responsible for circulating oil; if it malfunctions, oil pressure drops.
- Clogged Oil Filter:
- A dirty or clogged oil filter can restrict oil flow and reduce pressure.
- Worn Engine Components:
- Aging parts, such as bearings, may cause oil to escape, lowering pressure.
- Oil Pressure Sensor Malfunction:
- A faulty sensor may trigger the light even if pressure is normal.
- Using the Wrong Oil Type:
- Oil with incorrect viscosity may not circulate properly, especially in extreme temperatures.
What to Do When the Oil Pressure Light Turns On:
- Stop the Vehicle Immediately:
- Low oil pressure can quickly cause severe engine damage.
- Pull over safely and turn off the engine.
- Check the Oil Level:
- Open the hood and use the dipstick to check the oil level.
- If the level is low, add the appropriate type of oil to reach the recommended level.
- Inspect for Leaks:
- Look under the car for oil puddles or drips that may indicate a leak.
- Avoid Driving:
- Driving with insufficient oil pressure can lead to catastrophic engine failure.
- Seek Professional Help:
- If adding oil doesn’t turn off the light, have the vehicle towed to a mechanic to diagnose the issue.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Oil Changes:
- Follow your car manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals.
- Monitor Oil Levels:
- Check the oil level regularly, especially before long trips.
- Use the Correct Oil:
- Use oil with the recommended viscosity and specifications for your vehicle.
- Inspect for Leaks:
- Regularly check for oil leaks and address them promptly.
- Replace Filters and Sensors:
- Change the oil filter during each oil change and replace sensors as needed.
Ignoring the oil pressure warning light can lead to severe engine damage, so it’s crucial to act immediately when it appears.
Car Brake System Warning Light
Car Brake System Warning Light
Appearance:
- A red circle with an exclamation mark (!) or the letter “P” inside, sometimes accompanied by the word “BRAKE.”
- It may also appear as a red brake icon with a line representing brake pads.
Function:
The brake system warning light indicates an issue with the braking system. It can signal anything from a minor problem like the parking brake being engaged to serious issues such as brake fluid loss or system failure.
Common Causes:
- Parking Brake Engaged:
- The light is on if the parking brake is not fully released.
- Low Brake Fluid:
- Fluid levels may drop due to normal wear or leaks in the system.
- Worn Brake Pads:
- Some vehicles have sensors that trigger the light when brake pads are excessively worn.
- ABS System Fault:
- In some vehicles, the brake warning light works in conjunction with the ABS warning light, indicating an anti-lock braking system issue.
- Brake Hydraulic Pressure Loss:
- A significant drop in hydraulic pressure, possibly due to a fluid leak, can trigger the light.
- Sensor or Wiring Issues:
- Faulty sensors or damaged wiring can cause false warnings.
What to Do When the Brake System Light Turns On:
- Check the Parking Brake:
- Ensure the parking brake is fully released.
- Inspect the Brake Fluid Level:
- Open the hood and check the fluid reservoir. If the fluid is low, top it up with the recommended type of brake fluid.
- Test the Brakes:
- While driving slowly and safely, gently press the brake pedal to see if it feels normal or spongy.
- Look for Leaks:
- Check around the wheels and under the car for fluid leaks.
- Stop Driving If Necessary:
- If the brakes feel unresponsive or spongy, pull over and call for assistance.
- Consult a Mechanic:
- Even if the brakes feel fine after addressing minor issues, have the system inspected to ensure everything is in good working order.
When to Seek Immediate Help:
- The light remains on after topping up brake fluid or releasing the parking brake.
- The brakes feel weak, spongy, or unresponsive.
- There are signs of fluid leaks or unusual noises when braking.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Maintenance:
- Have the brake system inspected during routine service intervals.
- Monitor Brake Fluid Levels:
- Check the reservoir periodically and ensure there are no leaks.
- Replace Brake Pads and Rotors:
- Change pads and rotors as recommended to prevent excessive wear.
- Address Warning Signs Early:
- Squealing brakes, reduced responsiveness, or grinding noises indicate a need for immediate attention.
The brake system is critical for safety. If this light turns on and persists, prioritize addressing the issue immediately to ensure safe vehicle operation.
Car ABS Warning Light (Anti-lock Braking System)
Car ABS Warning Light (Anti-lock Braking System)
Appearance:
- A yellow or amber icon displaying the letters “ABS,” often within a circle and surrounded by parentheses.
Function:
The ABS warning light illuminates when there is a problem with the anti-lock braking system. The ABS is designed to prevent the wheels from locking up during hard braking, helping maintain steering control on slippery surfaces.
Common Causes:
- Faulty ABS Sensor:
- Each wheel has a sensor to monitor speed; a malfunctioning sensor can trigger the warning.
- Damaged Wheel Speed Sensor Wiring:
- Worn or damaged wiring can interrupt communication between sensors and the ABS module.
- ABS Module Failure:
- The control module that manages the ABS system may fail due to electrical issues or water ingress.
- Low Brake Fluid Levels:
- Insufficient brake fluid can affect ABS functionality.
- Blown Fuse or Relay Issues:
- A blown ABS fuse or relay can disable the system.
- Worn or Dirty Tone Ring:
- The tone ring, which works with the wheel speed sensors, may be damaged or dirty, leading to incorrect readings.
- System Malfunction During Start-up:
- If the ABS self-check fails when you start the car, the light may stay on.
What to Do When the ABS Warning Light Turns On:
- Check Brake Functionality:
- Test the brakes gently. If the ABS light is on but the brakes function normally, it’s likely an ABS-specific issue.
- If the brakes feel spongy or unresponsive, there may be a broader braking system problem.
- Inspect Brake Fluid Levels:
- Check the fluid reservoir under the hood. Add brake fluid if it’s low, using the recommended type.
- Drive Cautiously:
- If the light stays on, the ABS may not work, meaning you’re at greater risk of wheel lockup in emergency braking situations.
- Avoid Slippery Surfaces:
- Without ABS, the wheels may skid on wet or icy roads, reducing control.
- Consult a Mechanic:
- If the light persists, have the system inspected with a diagnostic scanner to identify the exact issue.
When to Seek Immediate Help:
- If the ABS warning light appears with the brake system warning light.
- If braking performance is noticeably affected.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular System Checks:
- Include the ABS in routine vehicle maintenance checks.
- Keep Sensors Clean:
- Ensure wheel speed sensors and tone rings are free of dirt and debris.
- Monitor Brake Fluid Levels:
- Keep the reservoir filled to prevent related ABS issues.
- Address ABS Issues Promptly:
- Don’t ignore the warning light; resolving small problems early prevents bigger repairs.
Note:
When the ABS warning light is on, your standard braking system will still function, but you lose the added safety of ABS in emergencies or on slippery roads. Prioritize repairs to restore full braking functionality.
Car Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) Light
Car Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) Light
Appearance:
- A yellow horseshoe-shaped icon with an exclamation mark (!) in the middle, or simply the letters “TPMS.”
Function:
The Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) light alerts you when one or more tires are under-inflated or over-inflated, which can affect vehicle safety, handling, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity.
Common Causes:
- Low Tire Pressure:
- Caused by temperature changes, punctures, or slow leaks.
- High Tire Pressure:
- Over-inflated tires can also trigger the TPMS light.
- Faulty TPMS Sensor:
- Sensors inside the tire may fail due to wear, damage, or battery depletion.
- Sensor Not Reset After Tire Service:
- TPMS needs recalibration after rotating or replacing tires.
- Sudden Air Pressure Loss:
- A puncture or blowout can cause rapid pressure loss, activating the light.
- System Calibration Issues:
- After tire replacement or rotation, the system may need to be reset.
What to Do When the TPMS Light Turns On:
- Check Tire Pressure:
- Use a tire pressure gauge to measure the pressure in all tires, including the spare (if it has a sensor).
- Compare readings to the recommended pressure listed in the owner’s manual or the placard on the driver’s door frame.
- Adjust Tire Pressure:
- Inflate or deflate the tires to the specified pressure levels.
- Inspect for Damage:
- Look for visible signs of punctures, cracks, or objects like nails embedded in the tire.
- Drive the Car:
- After adjusting the pressure, drive for a few miles to allow the TPMS to recalibrate. The light should turn off if the issue is resolved.
- Reset the TPMS:
- Some vehicles require manual reset via a button, menu, or OBD tool. Refer to your owner’s manual for instructions.
When to Seek Professional Help:
- The light stays on after adjusting the tire pressure.
- The TPMS icon blinks or flashes (indicates a system malfunction).
- You suspect a faulty sensor or internal system issue.
Preventive Measures:
- Check Tire Pressure Regularly:
- Use a reliable gauge, especially during seasonal temperature changes.
- Inspect Tires for Damage:
- Routine visual checks help catch issues early.
- Service the TPMS Sensors:
- Replace TPMS sensors every 5-10 years, as their internal batteries have limited lifespans.
- Maintain Proper Tire Maintenance:
- Rotate tires regularly and replace worn tires as recommended.
Note on Temperature Changes:
Tire pressure can drop by approximately 1 PSI for every 10°F decrease in temperature, which may trigger the TPMS light during cold weather. This is normal and can often be corrected by adjusting the tire pressure.
Car Coolant Temperature Warning Light
Car Coolant Temperature Warning Light
Appearance:
- A red or blue icon resembling a thermometer submerged in liquid, with wavy lines representing coolant.
Function:
The coolant temperature warning light alerts you when the engine’s temperature is too high or, in some cases, too low. It’s a critical warning that requires immediate attention to prevent engine damage.
Common Causes of the Light Turning On:
- Overheating Engine:
- Caused by low coolant levels, a faulty thermostat, or issues with the cooling system.
- Low Coolant Levels:
- Can result from leaks, improper filling, or extended periods without maintenance.
- Faulty Radiator:
- A clogged or damaged radiator may prevent proper heat dissipation.
- Broken Water Pump:
- The pump circulates coolant through the engine; a failure can lead to overheating.
- Thermostat Issues:
- A stuck thermostat can block coolant flow, causing overheating or overcooling.
- Coolant Sensor Malfunction:
- A faulty sensor may trigger a false warning.
- Cooling Fan Failure:
- If the fan doesn’t engage, especially in stop-and-go traffic, the engine may overheat.
What to Do When the Coolant Temperature Warning Light Comes On:
- Stop the Vehicle Safely:
- Pull over as soon as it’s safe to do so and turn off the engine.
- Check the Temperature Gauge:
- Confirm whether the engine is running hot (in the red zone) or cold.
- Let the Engine Cool:
- Wait at least 15-30 minutes before opening the hood to avoid burns from steam or hot coolant.
- Inspect Coolant Levels:
- Locate the coolant reservoir (usually a translucent plastic tank) and check the level. If low, add coolant mixed with water in the recommended ratio.
- Inspect for Leaks:
- Look under the vehicle for puddles of coolant or signs of a leak around hoses and the radiator.
- Call for Assistance:
- If the issue persists, avoid driving and contact a mechanic or roadside assistance.
What NOT to Do:
- Don’t Remove the Radiator Cap When Hot: The system is pressurized, and opening it while hot can cause scalding injuries.
- Don’t Continue Driving: Overheating can cause severe engine damage, including a blown head gasket or warped engine components.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Coolant Checks:
- Inspect levels monthly and before long trips. Top off with the correct type of coolant if needed.
- Scheduled Cooling System Maintenance:
- Replace the coolant as per the manufacturer’s recommendation (usually every 30,000–60,000 miles or every few years).
- Inspect Radiator and Hoses:
- Look for cracks, wear, or blockages in the cooling system.
- Ensure Proper Thermostat Function:
- Test or replace the thermostat during regular maintenance.
- Monitor Temperature Gauge:
- Stay alert to temperature fluctuations that may indicate a problem.
Cold Engine Indicator (Blue Light):
Some vehicles have a blue version of the coolant temperature light to indicate the engine is cold. This is not a warning but a reminder to drive gently until the engine reaches its optimal operating temperature.
The coolant temperature warning light is critical. Ignoring it can result in expensive repairs or even total engine failure. Always address the issue promptly!
Car Seat Belt Reminder Light
Car Seat Belt Reminder Light
Appearance:
- A red icon typically showing a seated figure with a diagonal line representing a seat belt across their chest, sometimes accompanied by a chime or beeping sound.
Function:
The seat belt reminder light is a safety feature designed to alert occupants that seat belts are not fastened. It ensures compliance with seat belt laws and promotes safety by reducing injury risks during accidents.
When the Light Activates:
- Driver or Passenger Not Wearing a Seat Belt:
- The light comes on if the driver or front passenger does not buckle their seat belt.
- Unfastened Rear Seat Belts (Optional):
- Some vehicles include reminders for rear passengers, especially in newer models.
- Heavy Objects on the Seat:
- The system may detect a bag or item on the seat as an “unbuckled passenger” and activate the light.
What to Do:
- Fasten Seat Belts:
- Ensure all occupants securely fasten their seat belts before driving.
- Remove Heavy Items from Seats:
- If the light activates due to an object, place it elsewhere in the vehicle.
- Check Seat Belt Connections:
- Inspect the buckle and belt for obstructions or damage that may prevent it from fastening properly.
If the Light Stays On:
- Faulty Seat Belt Sensor:
- The sensor in the seat or buckle may be malfunctioning.
- Electrical Issues:
- Wiring or system errors can cause the light to stay on even when belts are fastened.
- Check for System Alerts:
- Review your vehicle’s manual for troubleshooting or reset instructions.
If the issue persists, have the system inspected by a qualified technician.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Maintenance:
- Inspect seat belts and buckles for wear, fraying, or damage during routine service.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines:
- Use the seat belts as intended; improper use can damage the locking mechanism.
- Educate Passengers:
- Remind everyone in the vehicle to buckle up for safety and to avoid triggering the reminder light.
Safety Reminder:
The seat belt reminder light is more than a warning—it’s a lifesaving feature. Always ensure everyone in the vehicle is buckled up, as seat belts significantly reduce injury risk in accidents.
Car Airbag Warning Light
Car Airbag Warning Light
Appearance:
- A red or amber icon showing a seated figure with a circle (representing an airbag) in front of them, often labeled as “SRS” (Supplemental Restraint System).
Function:
The airbag warning light indicates a problem with the vehicle’s Supplemental Restraint System (SRS), which includes airbags and sometimes seatbelt pretensioners. If the light is on, one or more airbags may not deploy in an accident.
Common Causes:
- Faulty Airbag Sensors:
- Sensors in the car detect collisions and deploy the airbags. Malfunctions can cause the warning light to turn on.
- Damaged Airbag Module:
- The airbag control module may fail due to electrical problems, corrosion, or water damage.
- Seatbelt Pretensioner Issues:
- Faults in the seatbelt tensioning mechanism can trigger the warning.
- Wiring Problems:
- Loose, damaged, or corroded wiring in the SRS system can disrupt communication.
- Depleted Backup Battery:
- The airbag system’s backup battery may drain, especially if the main battery was recently replaced or discharged.
- Impact Without Deployment:
- Minor accidents that don’t deploy the airbags might still trigger the system and require a reset.
- Defective Clock Spring:
- The clock spring in the steering wheel, which connects the airbag to the electrical system, may wear out over time.
What to Do When the Airbag Warning Light Comes On:
- Don’t Ignore It:
- This light indicates a critical safety system fault. Driving with it on puts occupants at risk during an accident.
- Inspect for Other Issues:
- Check if the seatbelt pretensioners are functioning correctly or if the light coincides with other warning lights.
- Avoid Tampering:
- Don’t attempt to repair or reset the system yourself unless you are trained in SRS diagnostics.
- Seek Professional Help:
- Have the vehicle inspected by a certified technician. They can use specialized diagnostic tools to identify and resolve the issue.
When to Seek Immediate Help:
- The light remains illuminated after starting the car.
- It flashes continuously or comes on and off intermittently.
- You’ve recently been in a minor collision or have had repairs in the airbag area.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular System Checks:
- Include the airbag system in routine vehicle inspections.
- Avoid DIY Repairs:
- Airbag systems are sensitive and require professional handling.
- Keep Electrical Systems Healthy:
- Ensure the main and backup batteries are in good condition.
- Address Warning Lights Immediately:
- A small issue can escalate if ignored.
Important Notes:
- The vehicle is still drivable, but safety is compromised without a functioning airbag system.
- Airbags will likely not deploy if the warning light is on.
- Always refer to your owner’s manual for specific guidance related to your vehicle model.
Addressing the airbag warning light promptly ensures the system is ready to protect occupants in an accident.
Car Fuel Level Indicator
Car Fuel Level Indicator
Appearance:
- A gauge or digital display on the dashboard, typically showing a fuel tank symbol or a needle that points to various fuel levels (from “E” for Empty to “F” for Full).
- Some cars also show a digital readout of the exact fuel level or remaining miles before running out of fuel.
Function:
The fuel level indicator shows the amount of fuel left in the tank, giving drivers an idea of how much more driving they can do before needing to refuel. It is connected to a fuel sending unit in the tank, which measures the fuel level and sends the information to the gauge.
Common Issues:
- Sticking or Inaccurate Fuel Gauge:
- The needle may get stuck on “E” or “F,” or it may not move smoothly. This is often caused by a faulty fuel sending unit or a damaged float in the fuel tank.
- Fuel Sending Unit Failure:
- The sending unit, which measures the fuel level, may malfunction, causing the gauge to provide incorrect readings.
- Electrical Problems:
- Wiring issues, blown fuses, or a malfunctioning fuel gauge circuit can disrupt the fuel level readings.
- Faulty Fuel Gauge:
- The fuel gauge itself may fail, causing it to show incorrect readings regardless of the actual fuel level.
- Fuel Tank Calibration Issues:
- In some cases, especially after tank repairs or replacement, the system may need recalibration to give accurate readings.
What to Do When the Fuel Level Indicator is Malfunctioning:
- Check Fuel Level Manually:
- Use the fuel pump’s “miles until empty” readout (if available) or manually check fuel levels using a dipstick or the gas tank fill-up to estimate how much fuel is left.
- Try to Reset or Recalibrate:
- If you suspect a minor issue, such as a temporary glitch, try restarting the car or performing a reset according to the owner’s manual.
- Inspect for Obvious Issues:
- Check for any obvious electrical issues such as blown fuses or frayed wires under the dashboard or near the fuel tank area.
- Seek Professional Diagnosis:
- If the gauge is stuck on “empty” or “full,” or gives fluctuating readings, have a mechanic check the fuel sending unit, electrical components, and the gauge for issues.
When to Seek Immediate Help:
- The fuel gauge is giving consistently incorrect readings (e.g., showing “empty” when full or “full” when empty).
- You notice erratic fluctuations in the needle or digital display while driving.
- The fuel gauge has stopped working entirely.
Preventive Measures:
- Avoid Running the Tank Empty:
- Running the tank too low frequently can cause the fuel pump to draw in sediment, leading to clogs or damage to the fuel system, which may affect fuel readings.
- Monitor for Consistent Behavior:
- Pay attention to your fuel gauge’s behavior. If it starts to behave erratically, it’s an early indicator of a problem.
- Perform Regular Maintenance:
- Regularly inspect and replace worn-out sensors, wiring, or components connected to the fuel system.
Important Notes:
- Fuel Gauge Range: Many vehicles have a small reserve of fuel even when the gauge shows “empty.” However, relying on this reserve for extended periods can cause the fuel pump to overheat.
- Fuel Gauge Calibration: If you’ve recently had work done on the fuel tank, make sure the fuel gauge system is recalibrated to avoid incorrect readings.
A properly functioning fuel level indicator is crucial to avoiding running out of fuel unexpectedly, so addressing any malfunctions early helps prevent fuel system damage.
Car Door Ajar Warning Light
Car Door Ajar Warning Light
Appearance:
- A symbol of a car door with a small open or ajar sign (typically a door icon with a “key” or “open” indicator) or an illuminated light on the dashboard that resembles an open door.
Function:
The door ajar warning light indicates that one or more of the car doors (including the trunk or hatchback) is not fully closed or is open. This is a safety feature to alert you that the vehicle is not secure, and driving with an open door can be dangerous.
Common Causes:
- Door Not Fully Closed:
- One of the doors may be slightly ajar, either due to a poor seal or not being closed fully.
- Faulty Door Latch or Sensor:
- If the latch is damaged or the sensor in the door isn’t working properly, the car may falsely indicate that the door is open.
- Stuck or Malfunctioning Door:
- The door might be sticking due to dirt, ice, or damage, making it seem as though it is not fully closed when it actually is.
- Electrical or Wiring Issues:
- A problem with the wiring or the door’s electrical system can cause the warning light to illuminate even if the door is fully closed.
- Problems with Trunk or Tailgate:
- The warning light can also be triggered if the trunk or tailgate is not properly secured.
- Child Safety Locks or Latch Interference:
- In some cases, if the child safety locks are engaged, or there’s an obstruction in the door mechanism, the sensor may not read the door as closed.
What to Do When the Door Ajar Warning Light Turns On:
- Check All Doors:
- Physically check each door, including the trunk or tailgate, to ensure that they are fully closed.
- Inspect for Obstructions:
- Look for any debris, dirt, or ice around the door frame that may be preventing the door from closing properly.
- Check Door Latch Mechanism:
- Ensure that the door latch is functioning correctly and isn’t damaged or dirty. Clean if necessary.
- Test the Door Sensor:
- If you suspect the sensor is malfunctioning, try gently pressing the door to see if it resets. If the light persists, there may be an issue with the sensor.
- Look for Electrical Issues:
- Check for any loose or frayed wiring near the door or hinges that might affect the sensor’s ability to detect the door’s status.
When to Seek Professional Help:
- The light stays on even after all doors are securely closed: This could indicate a faulty door sensor or latch that requires repair or replacement.
- The door(s) don’t latch properly: If the doors won’t close securely, it might be a mechanical issue with the latch, and you should have it inspected.
- The light keeps flickering on and off: This could signal an electrical issue or a wiring problem that needs to be addressed.
Preventive Measures:
- Regularly Check Door Latches:
- Ensure that latches are functioning correctly and that the doors are closing smoothly without resistance.
- Keep Doors and Latches Clean:
- Regularly clean the door frames, latches, and seals to ensure they operate properly and to prevent dirt or ice from interfering with the door mechanism.
- Avoid Overloading the Doors:
- Avoid putting excess weight or pressure on the doors, especially in cold weather, as this can cause alignment or latch issues.
Important Notes:
- Child Safety Locks: If child safety locks are engaged on the rear doors, the door might appear to be open or ajar, even though it is fully closed.
- Weather Conditions: In extreme cold or wet weather, doors may freeze or become difficult to close completely, triggering the warning light.
The door ajar warning light is a safety feature that should not be ignored. Always ensure all doors and the trunk are properly secured before driving.
Car Traction Control System (TCS) or Stability Control Light
Car Traction Control System (TCS) or Stability Control Light
Appearance:
- Traction Control System (TCS) Light: A yellow or amber icon showing a car with squiggly lines behind the tires, symbolizing slipping or skidding.
- Stability Control Light: Often the same symbol, but may include additional letters, such as “ESP” (Electronic Stability Program) or “DSC” (Dynamic Stability Control) depending on the manufacturer.
Function:
Both the Traction Control System (TCS) and Electronic Stability Control (ESC) lights indicate that the vehicle’s systems designed to enhance traction and stability are engaged or experiencing a malfunction.
- Traction Control: Helps prevent wheel spin (especially during acceleration on slippery surfaces) by reducing engine power or applying brakes to individual wheels.
- Stability Control: Helps maintain vehicle stability when it detects skidding or loss of control, often by applying brakes to individual wheels or reducing engine power to avoid oversteering or understeering.
Common Causes for TCS or Stability Control Light:
- Slippery Road Conditions:
- The light may come on temporarily when driving on wet, icy, or slippery roads, as the system kicks in to help maintain control. The light may blink during this time.
- System Activation:
- When the system is working to maintain traction (such as during hard acceleration or driving on uneven terrain), the light may briefly flash to indicate it’s actively intervening.
- Malfunction in the TCS or ESC System:
- If the light stays on constantly, it could indicate a fault in the traction control or stability control systems. This could be caused by a sensor malfunction, wiring issue, or problem with the control module.
- Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor:
- Since both TCS and ESC rely on data from the wheel speed sensors to determine traction, a malfunctioning sensor could cause the system to trigger the warning light.
- Low Tire Pressure:
- Under-inflated tires can lead to inaccurate readings from the wheel speed sensors, causing the system to misinterpret traction and stability levels.
- Faulty Steering Angle Sensor:
- Stability control systems often use steering angle sensors to determine the driver’s intended path. If the sensor malfunctions, it can cause the system to malfunction as well.
- Bad ABS System:
- Since stability control often works alongside the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), problems with the ABS can also trigger the TCS or stability control warning light.
- Turning Off the System:
- Some vehicles allow drivers to manually deactivate TCS or ESC for certain driving conditions (such as off-roading or during racing). If the system is turned off, the light may remain on as a reminder.
What to Do When the TCS or Stability Control Light Comes On:
- Check for Slippery Conditions:
- If the light comes on briefly while driving on a slippery surface (such as ice, rain, or snow), this is normal, and the system is working to help maintain traction.
- Inspect Tire Pressure:
- Check the tire pressure and inflate tires to the recommended levels. Low tire pressure can affect wheel speed sensors and trigger the light.
- Look for System Malfunctions:
- If the light stays on or starts blinking while driving under normal conditions (i.e., no slippery roads), it may indicate a malfunction in the TCS or ESC system. In this case, you should have the vehicle inspected by a mechanic.
- Test the Vehicle’s Stability:
- If you notice the vehicle losing control or stability, avoid aggressive driving. Do not ignore the warning if the light stays on, as it may indicate that the stability control system is not functioning correctly.
- Turn Off and Restart:
- Sometimes, restarting the car can reset the system. If the light goes off after restarting, it could have been a temporary issue.
When to Seek Professional Help:
- The light stays on constantly: If the light stays illuminated, it suggests a malfunction, and the system may not be working to protect you. It’s best to get it checked by a mechanic.
- The light blinks frequently while driving: If the light blinks continuously even on dry roads, there may be an issue with the traction or stability control sensors or the system itself.
- Other Warning Lights Appear: If the TCS or ESC light comes on with other warning lights (e.g., ABS or Check Engine light), this could indicate a broader issue, and you should have the vehicle diagnosed by a professional.
Preventive Measures:
- Maintain Proper Tire Pressure:
- Regularly check and maintain tire pressure to ensure the TCS and stability control systems can function correctly.
- Regular Vehicle Maintenance:
- Ensure routine inspections of the ABS, wheel speed sensors, and stability control system, especially if you’ve noticed any unusual behavior while driving.
- Avoid Aggressive Driving:
- Abrupt acceleration, sharp turns, or high-speed cornering can trigger the system. Drive smoothly to reduce the likelihood of triggering the TCS or ESC system.
Important Notes:
- Temporary Warning: If the light flashes briefly, it often indicates that the system is actively helping to control traction. It’s usually nothing to worry about, but it’s worth paying attention to if it persists or starts blinking frequently.
- Driving Without Stability Control: If the system fails, it may impair the vehicle’s ability to correct for oversteering or understeering, making it more challenging to maintain control, especially on slippery or uneven surfaces.
Overall, the TCS and stability control systems are important for vehicle safety, especially under challenging driving conditions. If you notice issues with the system, it’s essential to address them promptly to maintain the effectiveness of these safety features.
12 Types Indicators Car Type Instrument Panel Function Part 2
The instrument panel of a car, often referred to as the dashboard, contains various indicators and warning lights that provide vital information about the vehicle’s status and operation. Here are 12 common types of indicators and their functions:
- Check Engine Light (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
- Function: Indicates an issue with the engine or emissions system.
- Action: Requires diagnostic attention to identify and fix the problem.
- Battery Warning Light
- Function: Signals a problem with the charging system, such as a failing battery or alternator.
- Action: Check the battery and charging system immediately.
- Oil Pressure Warning Light
- Function: Warns of low engine oil pressure, which could cause serious engine damage.
- Action: Stop the vehicle and check the oil level; add oil if necessary.
- Brake System Warning Light
- Function: Indicates issues like low brake fluid, a problem with the braking system, or that the parking brake is engaged.
- Action: Address immediately, especially if the light persists after releasing the parking brake.
- ABS Warning Light (Anti-lock Braking System)
- Function: Signals a malfunction in the ABS.
- Action: The brakes will still work, but the ABS may not function properly; have it checked.
- Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) Light
- Function: Alerts to low tire pressure in one or more tires.
- Action: Check and inflate tires to the recommended pressure.
- Coolant Temperature Warning Light
- Function: Warns of an overheating engine.
- Action: Stop the vehicle and let the engine cool; check coolant levels.
- Seat Belt Reminder Light
- Function: Alerts that the driver or passengers have not fastened their seat belts.
- Action: Buckle all seat belts.
- Airbag Warning Light
- Function: Indicates a fault in the airbag system.
- Action: Have the system inspected to ensure airbags will deploy in an accident.
- Fuel Level Indicator
- Function: Alerts when the fuel level is low.
- Action: Refuel soon to avoid running out.
- Door Ajar Warning Light
- Function: Indicates that one or more doors are not fully closed.
- Action: Check and close all doors securely.
- Traction Control System (TCS) or Stability Control Light
- Function: Signals the system is active to maintain traction or indicates a fault.
- Action: If it flashes during slippery conditions, it’s normal. If it stays on, check for system issues.
These indicators vary by car model, and it’s essential to refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific details on each light and its meaning.
Check Engine Light (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
Check Engine Light (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
Appearance:
- Typically an icon resembling an engine, often yellow or orange in color.
- May include text such as “CHECK ENGINE” or “SERVICE ENGINE SOON.”
Function:
- The check engine light (CEL) illuminates when the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics (OBD) system detects a problem with the engine or emissions control systems.
- It can indicate a minor issue (e.g., a loose gas cap) or a serious problem (e.g., engine misfire, catalytic converter failure).
Common Causes:
- Loose or Faulty Gas Cap:
- A loose or damaged gas cap can cause fuel vapors to leak, triggering the light.
- Oxygen Sensor Failure:
- The sensor monitors the amount of unburned oxygen in the exhaust.
- Mass Airflow Sensor Issues:
- This sensor measures the air entering the engine for proper fuel mixture.
- Spark Plug or Ignition Coil Problems:
- Faulty spark plugs or ignition coils can cause misfires.
- Catalytic Converter Problems:
- Failure can result in increased emissions and reduced engine performance.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve Issues:
- The valve helps reduce emissions by recirculating exhaust gases.
- Vacuum Leak:
- A leak in the engine’s vacuum system can disrupt air-fuel balance.
- Faulty Sensors or Wiring:
- Problems in various engine-related sensors or electrical connections.
What to Do When It Lights Up:
- Check for Simple Issues:
- Tighten the gas cap if it’s loose. Drive for a while to see if the light turns off.
- Monitor Vehicle Performance:
- If the vehicle runs normally, it may not be an urgent issue, but it still needs attention.
- If you notice poor acceleration, stalling, or other performance issues, avoid driving and seek help immediately.
- Use a Diagnostic Scanner:
- A code reader can pull error codes from the OBD system to identify the problem.
- Visit a Mechanic:
- If you’re unsure or if the issue persists, take the car to a qualified technician.
Flashing Check Engine Light:
- Indicates a severe issue, such as an engine misfire, which can cause significant damage.
- Stop driving immediately and get the vehicle serviced.
Preventive Measures:
- Perform regular maintenance, including oil changes, filter replacements, and spark plug checks.
- Address minor issues promptly to avoid bigger, costlier problems.
Car Battery Warning Light
Car Battery Warning Light
Appearance:
- A red icon resembling a car battery with positive (+) and negative (-) symbols.
Function:
The battery warning light indicates an issue with the vehicle’s charging system, not just the battery. When illuminated, it typically means the alternator isn’t charging the battery properly or there’s another problem in the electrical system.
Common Causes:
- Faulty Alternator:
- The alternator generates electricity to charge the battery and power electrical systems. A failure can trigger the warning light.
- Damaged Battery:
- An old or failing battery may not hold a charge, causing the system to detect an issue.
- Loose or Corroded Battery Connections:
- Poor contact can interrupt the flow of electricity.
- Drive Belt Issues:
- A broken or slipping drive belt can prevent the alternator from working properly.
- Faulty Voltage Regulator:
- The regulator ensures the alternator charges the battery at the correct voltage. Malfunctions can cause overcharging or undercharging.
- Wiring Problems:
- Loose, frayed, or damaged wiring in the charging system can disrupt its functionality.
What to Do When the Battery Light Turns On:
- Check for Immediate Symptoms:
- Dim headlights, flickering dashboard lights, or difficulty starting the engine are signs of a failing charging system.
- Turn Off Non-Essential Electrical Devices:
- Reduce the load on the battery by turning off accessories like the radio, air conditioning, and heated seats.
- Inspect the Battery Connections:
- If you’re comfortable, check if the battery terminals are tight and free of corrosion.
- Drive to Safety:
- The vehicle can run briefly on battery power, but it won’t last long. Head to a safe location or repair shop as soon as possible.
- Avoid Restarting the Engine:
- If the battery is nearly depleted, restarting the engine may not be possible.
When to Seek Immediate Help:
- The vehicle stalls or struggles to stay running.
- Electrical components, such as lights or the radio, fail completely.
- The warning light stays on after restarting the car.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Maintenance:
- Inspect the battery and alternator during routine servicing.
- Replace Old Batteries:
- Batteries typically last 3-5 years. Replace them before they fail.
- Check Belts and Connections:
- Ensure the drive belt is in good condition and connections are clean and secure.
- Monitor for Early Signs:
- Address flickering lights or difficulty starting the engine promptly.
A proactive approach can help avoid being stranded with a dead battery or failing charging system!
Car Oil Pressure Warning Light
Car Oil Pressure Warning Light
Appearance:
- An icon resembling an oil can with a drop of oil falling from its spout, typically red.
Function:
The oil pressure warning light indicates low oil pressure in the engine. Proper oil pressure is essential to lubricate engine components and prevent overheating or damage.
Common Causes:
- Low Oil Level:
- Insufficient oil in the system due to leaks, burning oil, or extended intervals between oil changes.
- Oil Pump Failure:
- The pump is responsible for circulating oil; if it malfunctions, oil pressure drops.
- Clogged Oil Filter:
- A dirty or clogged oil filter can restrict oil flow and reduce pressure.
- Worn Engine Components:
- Aging parts, such as bearings, may cause oil to escape, lowering pressure.
- Oil Pressure Sensor Malfunction:
- A faulty sensor may trigger the light even if pressure is normal.
- Using the Wrong Oil Type:
- Oil with incorrect viscosity may not circulate properly, especially in extreme temperatures.
What to Do When the Oil Pressure Light Turns On:
- Stop the Vehicle Immediately:
- Low oil pressure can quickly cause severe engine damage.
- Pull over safely and turn off the engine.
- Check the Oil Level:
- Open the hood and use the dipstick to check the oil level.
- If the level is low, add the appropriate type of oil to reach the recommended level.
- Inspect for Leaks:
- Look under the car for oil puddles or drips that may indicate a leak.
- Avoid Driving:
- Driving with insufficient oil pressure can lead to catastrophic engine failure.
- Seek Professional Help:
- If adding oil doesn’t turn off the light, have the vehicle towed to a mechanic to diagnose the issue.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Oil Changes:
- Follow your car manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals.
- Monitor Oil Levels:
- Check the oil level regularly, especially before long trips.
- Use the Correct Oil:
- Use oil with the recommended viscosity and specifications for your vehicle.
- Inspect for Leaks:
- Regularly check for oil leaks and address them promptly.
- Replace Filters and Sensors:
- Change the oil filter during each oil change and replace sensors as needed.
Ignoring the oil pressure warning light can lead to severe engine damage, so it’s crucial to act immediately when it appears.
Car Brake System Warning Light
Car Brake System Warning Light
Appearance:
- A red circle with an exclamation mark (!) or the letter “P” inside, sometimes accompanied by the word “BRAKE.”
- It may also appear as a red brake icon with a line representing brake pads.
Function:
The brake system warning light indicates an issue with the braking system. It can signal anything from a minor problem like the parking brake being engaged to serious issues such as brake fluid loss or system failure.
Common Causes:
- Parking Brake Engaged:
- The light is on if the parking brake is not fully released.
- Low Brake Fluid:
- Fluid levels may drop due to normal wear or leaks in the system.
- Worn Brake Pads:
- Some vehicles have sensors that trigger the light when brake pads are excessively worn.
- ABS System Fault:
- In some vehicles, the brake warning light works in conjunction with the ABS warning light, indicating an anti-lock braking system issue.
- Brake Hydraulic Pressure Loss:
- A significant drop in hydraulic pressure, possibly due to a fluid leak, can trigger the light.
- Sensor or Wiring Issues:
- Faulty sensors or damaged wiring can cause false warnings.
What to Do When the Brake System Light Turns On:
- Check the Parking Brake:
- Ensure the parking brake is fully released.
- Inspect the Brake Fluid Level:
- Open the hood and check the fluid reservoir. If the fluid is low, top it up with the recommended type of brake fluid.
- Test the Brakes:
- While driving slowly and safely, gently press the brake pedal to see if it feels normal or spongy.
- Look for Leaks:
- Check around the wheels and under the car for fluid leaks.
- Stop Driving If Necessary:
- If the brakes feel unresponsive or spongy, pull over and call for assistance.
- Consult a Mechanic:
- Even if the brakes feel fine after addressing minor issues, have the system inspected to ensure everything is in good working order.
When to Seek Immediate Help:
- The light remains on after topping up brake fluid or releasing the parking brake.
- The brakes feel weak, spongy, or unresponsive.
- There are signs of fluid leaks or unusual noises when braking.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Maintenance:
- Have the brake system inspected during routine service intervals.
- Monitor Brake Fluid Levels:
- Check the reservoir periodically and ensure there are no leaks.
- Replace Brake Pads and Rotors:
- Change pads and rotors as recommended to prevent excessive wear.
- Address Warning Signs Early:
- Squealing brakes, reduced responsiveness, or grinding noises indicate a need for immediate attention.
The brake system is critical for safety. If this light turns on and persists, prioritize addressing the issue immediately to ensure safe vehicle operation.
Car ABS Warning Light (Anti-lock Braking System)
Car ABS Warning Light (Anti-lock Braking System)
Appearance:
- A yellow or amber icon displaying the letters “ABS,” often within a circle and surrounded by parentheses.
Function:
The ABS warning light illuminates when there is a problem with the anti-lock braking system. The ABS is designed to prevent the wheels from locking up during hard braking, helping maintain steering control on slippery surfaces.
Common Causes:
- Faulty ABS Sensor:
- Each wheel has a sensor to monitor speed; a malfunctioning sensor can trigger the warning.
- Damaged Wheel Speed Sensor Wiring:
- Worn or damaged wiring can interrupt communication between sensors and the ABS module.
- ABS Module Failure:
- The control module that manages the ABS system may fail due to electrical issues or water ingress.
- Low Brake Fluid Levels:
- Insufficient brake fluid can affect ABS functionality.
- Blown Fuse or Relay Issues:
- A blown ABS fuse or relay can disable the system.
- Worn or Dirty Tone Ring:
- The tone ring, which works with the wheel speed sensors, may be damaged or dirty, leading to incorrect readings.
- System Malfunction During Start-up:
- If the ABS self-check fails when you start the car, the light may stay on.
What to Do When the ABS Warning Light Turns On:
- Check Brake Functionality:
- Test the brakes gently. If the ABS light is on but the brakes function normally, it’s likely an ABS-specific issue.
- If the brakes feel spongy or unresponsive, there may be a broader braking system problem.
- Inspect Brake Fluid Levels:
- Check the fluid reservoir under the hood. Add brake fluid if it’s low, using the recommended type.
- Drive Cautiously:
- If the light stays on, the ABS may not work, meaning you’re at greater risk of wheel lockup in emergency braking situations.
- Avoid Slippery Surfaces:
- Without ABS, the wheels may skid on wet or icy roads, reducing control.
- Consult a Mechanic:
- If the light persists, have the system inspected with a diagnostic scanner to identify the exact issue.
When to Seek Immediate Help:
- If the ABS warning light appears with the brake system warning light.
- If braking performance is noticeably affected.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular System Checks:
- Include the ABS in routine vehicle maintenance checks.
- Keep Sensors Clean:
- Ensure wheel speed sensors and tone rings are free of dirt and debris.
- Monitor Brake Fluid Levels:
- Keep the reservoir filled to prevent related ABS issues.
- Address ABS Issues Promptly:
- Don’t ignore the warning light; resolving small problems early prevents bigger repairs.
Note:
When the ABS warning light is on, your standard braking system will still function, but you lose the added safety of ABS in emergencies or on slippery roads. Prioritize repairs to restore full braking functionality.
Car Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) Light
Car Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) Light
Appearance:
- A yellow horseshoe-shaped icon with an exclamation mark (!) in the middle, or simply the letters “TPMS.”
Function:
The Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) light alerts you when one or more tires are under-inflated or over-inflated, which can affect vehicle safety, handling, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity.
Common Causes:
- Low Tire Pressure:
- Caused by temperature changes, punctures, or slow leaks.
- High Tire Pressure:
- Over-inflated tires can also trigger the TPMS light.
- Faulty TPMS Sensor:
- Sensors inside the tire may fail due to wear, damage, or battery depletion.
- Sensor Not Reset After Tire Service:
- TPMS needs recalibration after rotating or replacing tires.
- Sudden Air Pressure Loss:
- A puncture or blowout can cause rapid pressure loss, activating the light.
- System Calibration Issues:
- After tire replacement or rotation, the system may need to be reset.
What to Do When the TPMS Light Turns On:
- Check Tire Pressure:
- Use a tire pressure gauge to measure the pressure in all tires, including the spare (if it has a sensor).
- Compare readings to the recommended pressure listed in the owner’s manual or the placard on the driver’s door frame.
- Adjust Tire Pressure:
- Inflate or deflate the tires to the specified pressure levels.
- Inspect for Damage:
- Look for visible signs of punctures, cracks, or objects like nails embedded in the tire.
- Drive the Car:
- After adjusting the pressure, drive for a few miles to allow the TPMS to recalibrate. The light should turn off if the issue is resolved.
- Reset the TPMS:
- Some vehicles require manual reset via a button, menu, or OBD tool. Refer to your owner’s manual for instructions.
When to Seek Professional Help:
- The light stays on after adjusting the tire pressure.
- The TPMS icon blinks or flashes (indicates a system malfunction).
- You suspect a faulty sensor or internal system issue.
Preventive Measures:
- Check Tire Pressure Regularly:
- Use a reliable gauge, especially during seasonal temperature changes.
- Inspect Tires for Damage:
- Routine visual checks help catch issues early.
- Service the TPMS Sensors:
- Replace TPMS sensors every 5-10 years, as their internal batteries have limited lifespans.
- Maintain Proper Tire Maintenance:
- Rotate tires regularly and replace worn tires as recommended.
Note on Temperature Changes:
Tire pressure can drop by approximately 1 PSI for every 10°F decrease in temperature, which may trigger the TPMS light during cold weather. This is normal and can often be corrected by adjusting the tire pressure.
Car Coolant Temperature Warning Light
Car Coolant Temperature Warning Light
Appearance:
- A red or blue icon resembling a thermometer submerged in liquid, with wavy lines representing coolant.
Function:
The coolant temperature warning light alerts you when the engine’s temperature is too high or, in some cases, too low. It’s a critical warning that requires immediate attention to prevent engine damage.
Common Causes of the Light Turning On:
- Overheating Engine:
- Caused by low coolant levels, a faulty thermostat, or issues with the cooling system.
- Low Coolant Levels:
- Can result from leaks, improper filling, or extended periods without maintenance.
- Faulty Radiator:
- A clogged or damaged radiator may prevent proper heat dissipation.
- Broken Water Pump:
- The pump circulates coolant through the engine; a failure can lead to overheating.
- Thermostat Issues:
- A stuck thermostat can block coolant flow, causing overheating or overcooling.
- Coolant Sensor Malfunction:
- A faulty sensor may trigger a false warning.
- Cooling Fan Failure:
- If the fan doesn’t engage, especially in stop-and-go traffic, the engine may overheat.
What to Do When the Coolant Temperature Warning Light Comes On:
- Stop the Vehicle Safely:
- Pull over as soon as it’s safe to do so and turn off the engine.
- Check the Temperature Gauge:
- Confirm whether the engine is running hot (in the red zone) or cold.
- Let the Engine Cool:
- Wait at least 15-30 minutes before opening the hood to avoid burns from steam or hot coolant.
- Inspect Coolant Levels:
- Locate the coolant reservoir (usually a translucent plastic tank) and check the level. If low, add coolant mixed with water in the recommended ratio.
- Inspect for Leaks:
- Look under the vehicle for puddles of coolant or signs of a leak around hoses and the radiator.
- Call for Assistance:
- If the issue persists, avoid driving and contact a mechanic or roadside assistance.
What NOT to Do:
- Don’t Remove the Radiator Cap When Hot: The system is pressurized, and opening it while hot can cause scalding injuries.
- Don’t Continue Driving: Overheating can cause severe engine damage, including a blown head gasket or warped engine components.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Coolant Checks:
- Inspect levels monthly and before long trips. Top off with the correct type of coolant if needed.
- Scheduled Cooling System Maintenance:
- Replace the coolant as per the manufacturer’s recommendation (usually every 30,000–60,000 miles or every few years).
- Inspect Radiator and Hoses:
- Look for cracks, wear, or blockages in the cooling system.
- Ensure Proper Thermostat Function:
- Test or replace the thermostat during regular maintenance.
- Monitor Temperature Gauge:
- Stay alert to temperature fluctuations that may indicate a problem.
Cold Engine Indicator (Blue Light):
Some vehicles have a blue version of the coolant temperature light to indicate the engine is cold. This is not a warning but a reminder to drive gently until the engine reaches its optimal operating temperature.
The coolant temperature warning light is critical. Ignoring it can result in expensive repairs or even total engine failure. Always address the issue promptly!
Car Seat Belt Reminder Light
Car Seat Belt Reminder Light
Appearance:
- A red icon typically showing a seated figure with a diagonal line representing a seat belt across their chest, sometimes accompanied by a chime or beeping sound.
Function:
The seat belt reminder light is a safety feature designed to alert occupants that seat belts are not fastened. It ensures compliance with seat belt laws and promotes safety by reducing injury risks during accidents.
When the Light Activates:
- Driver or Passenger Not Wearing a Seat Belt:
- The light comes on if the driver or front passenger does not buckle their seat belt.
- Unfastened Rear Seat Belts (Optional):
- Some vehicles include reminders for rear passengers, especially in newer models.
- Heavy Objects on the Seat:
- The system may detect a bag or item on the seat as an “unbuckled passenger” and activate the light.
What to Do:
- Fasten Seat Belts:
- Ensure all occupants securely fasten their seat belts before driving.
- Remove Heavy Items from Seats:
- If the light activates due to an object, place it elsewhere in the vehicle.
- Check Seat Belt Connections:
- Inspect the buckle and belt for obstructions or damage that may prevent it from fastening properly.
If the Light Stays On:
- Faulty Seat Belt Sensor:
- The sensor in the seat or buckle may be malfunctioning.
- Electrical Issues:
- Wiring or system errors can cause the light to stay on even when belts are fastened.
- Check for System Alerts:
- Review your vehicle’s manual for troubleshooting or reset instructions.
If the issue persists, have the system inspected by a qualified technician.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Maintenance:
- Inspect seat belts and buckles for wear, fraying, or damage during routine service.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines:
- Use the seat belts as intended; improper use can damage the locking mechanism.
- Educate Passengers:
- Remind everyone in the vehicle to buckle up for safety and to avoid triggering the reminder light.
Safety Reminder:
The seat belt reminder light is more than a warning—it’s a lifesaving feature. Always ensure everyone in the vehicle is buckled up, as seat belts significantly reduce injury risk in accidents.
Car Airbag Warning Light
Car Airbag Warning Light
Appearance:
- A red or amber icon showing a seated figure with a circle (representing an airbag) in front of them, often labeled as “SRS” (Supplemental Restraint System).
Function:
The airbag warning light indicates a problem with the vehicle’s Supplemental Restraint System (SRS), which includes airbags and sometimes seatbelt pretensioners. If the light is on, one or more airbags may not deploy in an accident.
Common Causes:
- Faulty Airbag Sensors:
- Sensors in the car detect collisions and deploy the airbags. Malfunctions can cause the warning light to turn on.
- Damaged Airbag Module:
- The airbag control module may fail due to electrical problems, corrosion, or water damage.
- Seatbelt Pretensioner Issues:
- Faults in the seatbelt tensioning mechanism can trigger the warning.
- Wiring Problems:
- Loose, damaged, or corroded wiring in the SRS system can disrupt communication.
- Depleted Backup Battery:
- The airbag system’s backup battery may drain, especially if the main battery was recently replaced or discharged.
- Impact Without Deployment:
- Minor accidents that don’t deploy the airbags might still trigger the system and require a reset.
- Defective Clock Spring:
- The clock spring in the steering wheel, which connects the airbag to the electrical system, may wear out over time.
What to Do When the Airbag Warning Light Comes On:
- Don’t Ignore It:
- This light indicates a critical safety system fault. Driving with it on puts occupants at risk during an accident.
- Inspect for Other Issues:
- Check if the seatbelt pretensioners are functioning correctly or if the light coincides with other warning lights.
- Avoid Tampering:
- Don’t attempt to repair or reset the system yourself unless you are trained in SRS diagnostics.
- Seek Professional Help:
- Have the vehicle inspected by a certified technician. They can use specialized diagnostic tools to identify and resolve the issue.
When to Seek Immediate Help:
- The light remains illuminated after starting the car.
- It flashes continuously or comes on and off intermittently.
- You’ve recently been in a minor collision or have had repairs in the airbag area.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular System Checks:
- Include the airbag system in routine vehicle inspections.
- Avoid DIY Repairs:
- Airbag systems are sensitive and require professional handling.
- Keep Electrical Systems Healthy:
- Ensure the main and backup batteries are in good condition.
- Address Warning Lights Immediately:
- A small issue can escalate if ignored.
Important Notes:
- The vehicle is still drivable, but safety is compromised without a functioning airbag system.
- Airbags will likely not deploy if the warning light is on.
- Always refer to your owner’s manual for specific guidance related to your vehicle model.
Addressing the airbag warning light promptly ensures the system is ready to protect occupants in an accident.
Car Fuel Level Indicator
Car Fuel Level Indicator
Appearance:
- A gauge or digital display on the dashboard, typically showing a fuel tank symbol or a needle that points to various fuel levels (from “E” for Empty to “F” for Full).
- Some cars also show a digital readout of the exact fuel level or remaining miles before running out of fuel.
Function:
The fuel level indicator shows the amount of fuel left in the tank, giving drivers an idea of how much more driving they can do before needing to refuel. It is connected to a fuel sending unit in the tank, which measures the fuel level and sends the information to the gauge.
Common Issues:
- Sticking or Inaccurate Fuel Gauge:
- The needle may get stuck on “E” or “F,” or it may not move smoothly. This is often caused by a faulty fuel sending unit or a damaged float in the fuel tank.
- Fuel Sending Unit Failure:
- The sending unit, which measures the fuel level, may malfunction, causing the gauge to provide incorrect readings.
- Electrical Problems:
- Wiring issues, blown fuses, or a malfunctioning fuel gauge circuit can disrupt the fuel level readings.
- Faulty Fuel Gauge:
- The fuel gauge itself may fail, causing it to show incorrect readings regardless of the actual fuel level.
- Fuel Tank Calibration Issues:
- In some cases, especially after tank repairs or replacement, the system may need recalibration to give accurate readings.
What to Do When the Fuel Level Indicator is Malfunctioning:
- Check Fuel Level Manually:
- Use the fuel pump’s “miles until empty” readout (if available) or manually check fuel levels using a dipstick or the gas tank fill-up to estimate how much fuel is left.
- Try to Reset or Recalibrate:
- If you suspect a minor issue, such as a temporary glitch, try restarting the car or performing a reset according to the owner’s manual.
- Inspect for Obvious Issues:
- Check for any obvious electrical issues such as blown fuses or frayed wires under the dashboard or near the fuel tank area.
- Seek Professional Diagnosis:
- If the gauge is stuck on “empty” or “full,” or gives fluctuating readings, have a mechanic check the fuel sending unit, electrical components, and the gauge for issues.
When to Seek Immediate Help:
- The fuel gauge is giving consistently incorrect readings (e.g., showing “empty” when full or “full” when empty).
- You notice erratic fluctuations in the needle or digital display while driving.
- The fuel gauge has stopped working entirely.
Preventive Measures:
- Avoid Running the Tank Empty:
- Running the tank too low frequently can cause the fuel pump to draw in sediment, leading to clogs or damage to the fuel system, which may affect fuel readings.
- Monitor for Consistent Behavior:
- Pay attention to your fuel gauge’s behavior. If it starts to behave erratically, it’s an early indicator of a problem.
- Perform Regular Maintenance:
- Regularly inspect and replace worn-out sensors, wiring, or components connected to the fuel system.
Important Notes:
- Fuel Gauge Range: Many vehicles have a small reserve of fuel even when the gauge shows “empty.” However, relying on this reserve for extended periods can cause the fuel pump to overheat.
- Fuel Gauge Calibration: If you’ve recently had work done on the fuel tank, make sure the fuel gauge system is recalibrated to avoid incorrect readings.
A properly functioning fuel level indicator is crucial to avoiding running out of fuel unexpectedly, so addressing any malfunctions early helps prevent fuel system damage.
Car Door Ajar Warning Light
Car Door Ajar Warning Light
Appearance:
- A symbol of a car door with a small open or ajar sign (typically a door icon with a “key” or “open” indicator) or an illuminated light on the dashboard that resembles an open door.
Function:
The door ajar warning light indicates that one or more of the car doors (including the trunk or hatchback) is not fully closed or is open. This is a safety feature to alert you that the vehicle is not secure, and driving with an open door can be dangerous.
Common Causes:
- Door Not Fully Closed:
- One of the doors may be slightly ajar, either due to a poor seal or not being closed fully.
- Faulty Door Latch or Sensor:
- If the latch is damaged or the sensor in the door isn’t working properly, the car may falsely indicate that the door is open.
- Stuck or Malfunctioning Door:
- The door might be sticking due to dirt, ice, or damage, making it seem as though it is not fully closed when it actually is.
- Electrical or Wiring Issues:
- A problem with the wiring or the door’s electrical system can cause the warning light to illuminate even if the door is fully closed.
- Problems with Trunk or Tailgate:
- The warning light can also be triggered if the trunk or tailgate is not properly secured.
- Child Safety Locks or Latch Interference:
- In some cases, if the child safety locks are engaged, or there’s an obstruction in the door mechanism, the sensor may not read the door as closed.
What to Do When the Door Ajar Warning Light Turns On:
- Check All Doors:
- Physically check each door, including the trunk or tailgate, to ensure that they are fully closed.
- Inspect for Obstructions:
- Look for any debris, dirt, or ice around the door frame that may be preventing the door from closing properly.
- Check Door Latch Mechanism:
- Ensure that the door latch is functioning correctly and isn’t damaged or dirty. Clean if necessary.
- Test the Door Sensor:
- If you suspect the sensor is malfunctioning, try gently pressing the door to see if it resets. If the light persists, there may be an issue with the sensor.
- Look for Electrical Issues:
- Check for any loose or frayed wiring near the door or hinges that might affect the sensor’s ability to detect the door’s status.
When to Seek Professional Help:
- The light stays on even after all doors are securely closed: This could indicate a faulty door sensor or latch that requires repair or replacement.
- The door(s) don’t latch properly: If the doors won’t close securely, it might be a mechanical issue with the latch, and you should have it inspected.
- The light keeps flickering on and off: This could signal an electrical issue or a wiring problem that needs to be addressed.
Preventive Measures:
- Regularly Check Door Latches:
- Ensure that latches are functioning correctly and that the doors are closing smoothly without resistance.
- Keep Doors and Latches Clean:
- Regularly clean the door frames, latches, and seals to ensure they operate properly and to prevent dirt or ice from interfering with the door mechanism.
- Avoid Overloading the Doors:
- Avoid putting excess weight or pressure on the doors, especially in cold weather, as this can cause alignment or latch issues.
Important Notes:
- Child Safety Locks: If child safety locks are engaged on the rear doors, the door might appear to be open or ajar, even though it is fully closed.
- Weather Conditions: In extreme cold or wet weather, doors may freeze or become difficult to close completely, triggering the warning light.
The door ajar warning light is a safety feature that should not be ignored. Always ensure all doors and the trunk are properly secured before driving.
Car Traction Control System (TCS) or Stability Control Light
Car Traction Control System (TCS) or Stability Control Light
Appearance:
- Traction Control System (TCS) Light: A yellow or amber icon showing a car with squiggly lines behind the tires, symbolizing slipping or skidding.
- Stability Control Light: Often the same symbol, but may include additional letters, such as “ESP” (Electronic Stability Program) or “DSC” (Dynamic Stability Control) depending on the manufacturer.
Function:
Both the Traction Control System (TCS) and Electronic Stability Control (ESC) lights indicate that the vehicle’s systems designed to enhance traction and stability are engaged or experiencing a malfunction.
- Traction Control: Helps prevent wheel spin (especially during acceleration on slippery surfaces) by reducing engine power or applying brakes to individual wheels.
- Stability Control: Helps maintain vehicle stability when it detects skidding or loss of control, often by applying brakes to individual wheels or reducing engine power to avoid oversteering or understeering.
Common Causes for TCS or Stability Control Light:
- Slippery Road Conditions:
- The light may come on temporarily when driving on wet, icy, or slippery roads, as the system kicks in to help maintain control. The light may blink during this time.
- System Activation:
- When the system is working to maintain traction (such as during hard acceleration or driving on uneven terrain), the light may briefly flash to indicate it’s actively intervening.
- Malfunction in the TCS or ESC System:
- If the light stays on constantly, it could indicate a fault in the traction control or stability control systems. This could be caused by a sensor malfunction, wiring issue, or problem with the control module.
- Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor:
- Since both TCS and ESC rely on data from the wheel speed sensors to determine traction, a malfunctioning sensor could cause the system to trigger the warning light.
- Low Tire Pressure:
- Under-inflated tires can lead to inaccurate readings from the wheel speed sensors, causing the system to misinterpret traction and stability levels.
- Faulty Steering Angle Sensor:
- Stability control systems often use steering angle sensors to determine the driver’s intended path. If the sensor malfunctions, it can cause the system to malfunction as well.
- Bad ABS System:
- Since stability control often works alongside the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), problems with the ABS can also trigger the TCS or stability control warning light.
- Turning Off the System:
- Some vehicles allow drivers to manually deactivate TCS or ESC for certain driving conditions (such as off-roading or during racing). If the system is turned off, the light may remain on as a reminder.
What to Do When the TCS or Stability Control Light Comes On:
- Check for Slippery Conditions:
- If the light comes on briefly while driving on a slippery surface (such as ice, rain, or snow), this is normal, and the system is working to help maintain traction.
- Inspect Tire Pressure:
- Check the tire pressure and inflate tires to the recommended levels. Low tire pressure can affect wheel speed sensors and trigger the light.
- Look for System Malfunctions:
- If the light stays on or starts blinking while driving under normal conditions (i.e., no slippery roads), it may indicate a malfunction in the TCS or ESC system. In this case, you should have the vehicle inspected by a mechanic.
- Test the Vehicle’s Stability:
- If you notice the vehicle losing control or stability, avoid aggressive driving. Do not ignore the warning if the light stays on, as it may indicate that the stability control system is not functioning correctly.
- Turn Off and Restart:
- Sometimes, restarting the car can reset the system. If the light goes off after restarting, it could have been a temporary issue.
When to Seek Professional Help:
- The light stays on constantly: If the light stays illuminated, it suggests a malfunction, and the system may not be working to protect you. It’s best to get it checked by a mechanic.
- The light blinks frequently while driving: If the light blinks continuously even on dry roads, there may be an issue with the traction or stability control sensors or the system itself.
- Other Warning Lights Appear: If the TCS or ESC light comes on with other warning lights (e.g., ABS or Check Engine light), this could indicate a broader issue, and you should have the vehicle diagnosed by a professional.
Preventive Measures:
- Maintain Proper Tire Pressure:
- Regularly check and maintain tire pressure to ensure the TCS and stability control systems can function correctly.
- Regular Vehicle Maintenance:
- Ensure routine inspections of the ABS, wheel speed sensors, and stability control system, especially if you’ve noticed any unusual behavior while driving.
- Avoid Aggressive Driving:
- Abrupt acceleration, sharp turns, or high-speed cornering can trigger the system. Drive smoothly to reduce the likelihood of triggering the TCS or ESC system.
Important Notes:
- Temporary Warning: If the light flashes briefly, it often indicates that the system is actively helping to control traction. It’s usually nothing to worry about, but it’s worth paying attention to if it persists or starts blinking frequently.
- Driving Without Stability Control: If the system fails, it may impair the vehicle’s ability to correct for oversteering or understeering, making it more challenging to maintain control, especially on slippery or uneven surfaces.
Overall, the TCS and stability control systems are important for vehicle safety, especially under challenging driving conditions. If you notice issues with the system, it’s essential to address them promptly to maintain the effectiveness of these safety features.
Well that’s just an example of the types of car and motorcycle indicator indicators above that are often encountered in general when first starting the car engine of course there are some Indicators that light up a few seconds to indicate that the indicator is working properly. Thanks for visiting (Technology Automotive).